
Eating a healthy diet offers a wide variety of benefits for physical health, mental health and is crucial for overall well-being. In this blog post, I will be covering topics about how to eat a healthy diet, the benefits of a high fiber, high protein diet, how to make a healthy plate and featuring my COLLECTION OF HEALTHY, HIGH-FIBER, HIGH-PROTEIN RECIPES. (See end of post for recipe books)
Some key advantages of adopting and sustaining a healthy diet that includes plenty of fiber and protein are; the intake of essential nutrients, weight management, reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, blood sugar control, better digestive health, good bone health, improved cognitive function, reduced risk of chronic diseases, reduced skin aging and acne and improvement in mental health.
What is a considered a Healthy Diet?
This answer is going to vary depending on who you speak to. As an integrative nutritionist and personal trainer that’s studied health and fitness and worked with a variety of clientele over twenty plus years, I’m going to define a healthy diet based on a diet that not only gives you a healthy body composition but also nourishes you from the inside out and prevents against disease.
A healthy diet is one that provides the necessary nutrients, vitamins, and minerals the body needs to function optimally while minimizing the risk of chronic diseases. A balanced and healthy diet typically includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods from all food groups. Here are the key components of a healthy diet:
Fruits and Vegetables: Aim to include a colorful array of fruits and vegetables, as different colors indicate different nutrients. Try to get in at least 5 servings of fruits and vegetables per day.
Whole Grains: Choose whole grains over refined grains for higher fiber content and better nutrient profile. Examples: Brown rice, quinoa and oats. I personally avoid gluten but I will have einkorn pasta and sourdough on rare occasions.
Lean Proteins: Include sources of lean protein, such as poultry, fish, lean meats, organic soy, beans, and legumes.
Healthy Fats: Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated Fats – Choose sources like olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds.
Portion Control: Portion control plays a big part in a healthy diet as well. I’ll address this more below on how to build a healthy plate.
Benefits of Eating a Healthy Diet
Eating healthy offers a myriad of benefits that contribute to overall well-being. A nutritious diet supports weight management by providing essential nutrients without excess calories, reducing the risk of obesity and related health issues. Additionally, here are some benefits of eating healthy:
Weight Management
Healthy eating supports weight control by providing essential nutrients without excess calories. It helps prevent obesity and related health issues.
Improved Heart Health
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can lower the risk of heart disease by reducing cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and inflammation.
Better Digestive Health
High-fiber foods promote healthy digestion, prevent constipation, and support a diverse gut microbiome, which is linked to overall well-being.
Stronger Immune System
Proper nutrition supports a robust immune system, helping the body defend against infections and illnesses.
Healthy Skin, Hair, and Nails
Nutrient-rich foods contribute to the health and appearance of the skin, hair, and nails. Antioxidants help protect against damage from free radicals.

Benefits of a High Fiber Diet
Fiber is an essential component of a healthy diet and offers numerous benefits for overall well-being. Here are some key advantages of including an adequate amount of fiber in your diet:
Digestive Health
Prevention of Constipation, diverticulitis and hemorroids: Fiber adds bulk to the stool, softening it and aiding in regular bowel movements.
Weight Management & Appetite Control
High-fiber foods are more filling, which can help control appetite and contribute to weight management by promoting a feeling of fullness. High-fiber foods such as fruits and vegetables have a lower caloric density making them beneficial for those seeking to manage their weight.
Blood Sugar Control
Soluble fiber, found in oats, beans, and certain fruits, can help regulate blood sugar levels by slowing the absorption of glucose.
Heart Health
Cholesterol Reduction & Blood Pressure Regulation: Soluble fiber can help lower blood cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol and promoting its excretion. A diet rich in fiber may lower blood pressure as well. This, in turn, can reduce the risk of heart disease.
Promotes a Healthy Gut Microbiota
Fiber serves as a prebiotic, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. A balanced and diverse gut microbiota is linked to overall health, a reduction in inflammation and a robust immune system.
Prevention of Certain Diseases
Adequate fiber intake is associated with a lower risk of developing colorectal cancer and type 2 diabetes.
To reap the benefits of fiber, it’s important to include a variety of fiber-rich foods in your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts. Additionally, staying adequately hydrated is crucial to support the effectiveness of fiber in promoting digestive health.
How much Fiber is recommended?
The USDA’s Dietary Guidelines for AmericansTrusted Source suggest the following amounts of fiber:
Women under 50: 25 to 28 grams per day
Men under 50: 31 to 34 grams per day
Women 51 and older: 22 grams per day
Men 51 and older: 28 grams per day
Note: If you suffer from ulcerative colitis, Cohn’s disease, or irritable bowel syndrome, you should avoid a high-fiber diet.
Benefits of a High-Protein Diet
A high-protein diet offers several benefits for overall health, fitness, and well-being. Here are some key advantages of incorporating sufficient protein into your diet:
Muscle Growth and Repair
Protein Synthesis: Proteins are crucial for the synthesis of new proteins in the body, including those responsible for muscle growth, repair, and maintenance.
Weight Management
Appetite Regulation: Protein has a satiating effect, helping to control appetite and reduce overall calorie intake. This can be beneficial for weight management and weight loss.
Fat Loss
Preservation of Lean Body Mass: When individuals are in a calorie deficit for weight loss, a higher protein intake helps preserve lean muscle mass, ensuring that the weight lost comes primarily from fat rather than muscle.
Blood Sugar Regulation:
Improved Insulin Sensitivity & Blood Glucose Control: Protein consumption, especially when combined with resistance training, can improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Including protein in your meals helps stabilize blood sugar levels.
Bone Health:
Calcium Absorption: Protein positively influences calcium absorption, contributing to bone health and potentially reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
It’s important to note that individual protein needs can vary based on factors such as age, weight, activity level, and health status. Before participating in a high-protein diet, consider consulting with your doctor. Additionally, sourcing protein from a variety of food sources, including lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, legumes, and plant-based sources, can contribute to a well-rounded and nutritious diet.
Note: A high-protein diet is not a good idea for someone with kidney disease. Also, someone with heart disease or high cholesterol needs to be mindful of the protein sources. In this case I would encourage plenty of plant protein sources and minimal lean animal protein sources. My husband has heart disease (genetic – hypercholesterolemia). I have him on a heavy plant diet with lots of plant proteins. He still eats lean animal protein just not in large amounts.
How Much Protein Do You Need?
The recommended daily protein intake can vary based on several factors, including age, weight, activity level, and overall health. According to an updated clinical study published in 2017 the reference values for the intake of protein for adults under the age of 65 is .8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. Adults over the age of 65 require 1 gram of protein per kilogram of body weight per day.
Active Individuals or Athletes:
Individuals who engage in regular exercise or intense physical activity may require more protein to support muscle repair and growth. The protein needs for active individuals can range from 1.2 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day.
Weight Loss for Females
To make things a little simpler. This is the formula I use for myself and my female clients that want to lose weight. I have them take .73 – 1 grams of protein per pound of body weight. If weight loss is your goal, go off of your goal weight. You’ll need to be in a calorie deficit as well.
For example I weigh somewhere between 140 – 145lbs, depending on the time of the month. My goal weight is around 135lbs. Therefore I eat at least 98-135 grams of protein per day. I’m on the higher end on workout days and on the lower end on less active days. I also personally like to mix both plant and animal protein to get my protein needs in. Too much animal protein can sometimes lead to chronic diseases, therefore I strive to get a good intake of both plant and animal protein.
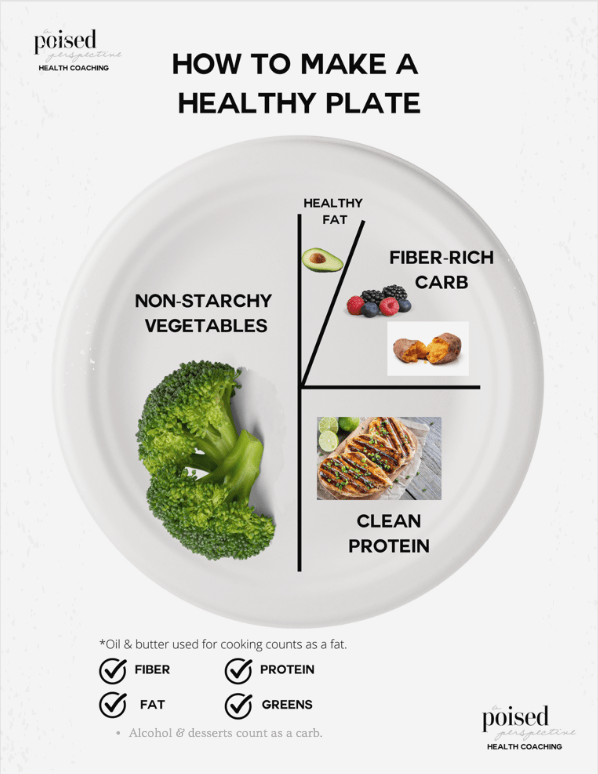
How to Make a Healthy Plate
Building a healthy plate involves creating a well-balanced and nutritious meal that provides essential nutrients, supports overall health, and helps maintain a healthy weight. My guidelines for building a healthy plate can help you construct a healthy and balanced plate and achieve a healthy body composition.
- Fill half your plate with non-starchy veggies. I like to encourage my clients to go for those dark nutrient dense greens like kale, spinach, broccoli, green beans, asparagus, brussel sprouts, arugula, collard greens and even cabbage.
- Choose a healthy, fiber rich carbohydrate and fill one-fourth of your plate with it.
- Choose a healthy lean protein and try to make sure it’s at least 20 grams. I personally try to shoot for 25-30g of protein at each meal.
- Do you need to add a healthy fat or have you used a healthy fat like olive oil for cooking already? Often people forget about the fat they’ve used for cooking. If you haven’t used a healthy fat for cooking, you could add 1/4 of an avocado or 1/4 cup of nuts.
See my suggestions below for healthy versions of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats.
Carbs
- Oatmeal
- Yams
- Brown Rice
- Sweet Potatoes, White Potatoes
- Multigrain hot cereal
- White potatoes with skin
- Whole grain or gluten free Bread
- Whole grain, gluten free, or einkorn pasta
- Beans and lentils
- Cream of rice hot cereal
- Quinoa
- Couscous
- Pumpkin
- Butternut, Acorn squash
- Fresh beets
- Peas
- Turnips
- Corn
- Fruit
Protein
- Eggs
- Organic protein powder
- Chicken Breast
- Salmon
- Turkey breast
- Canned Tuna
- Nuts & Nut Butters
- Seeds
- Edamame
- Beans
- Spirulina powder
- Nutritional Yeast
- Chickpeas
- Tofu
- Top round steak
- Flank Steak
- Codfish
- Greek yogurt
- Rainbow trout
- Cottage Cheese
- Bison/Buffalo
Healthy Fats
- Flaxseed, Chia seeds
- Olive oil
- Avocado
- Avocado oil
- Virgin coconut oil
- Clarified butter
- Ripe Olives
- Peanut oil
- Hemp Seedoil
- Nuts – Pecans, Cashews, Pistachios, Walnuts, Peanuts, Macadamia nuts
- Cheese
- Whole eggs
- Dark Chocolate
- Fatty Fish – Salmon, trout, mackeral, sardines, herring)
- Full fat yogurt
A Few of my Favorite Healthy Pantry Staples
If you need help finding some healthy items for on the go, here are some of my favorite healthy pantry staples.

Lesser Evil Popcorn Snacks | Mary’s Gone Crackers | Safe Catch Tuna | The New Primal Turkey Sticks | Orgain Protein Shake | That’s It Bars | Edamame Beans | Aloha Protein Bars | Roastery Coast Nuts | Quest Protein Chips | Kettle & Fire Bone Broth | Nick’s Protein Bars

Kitchen Essentials for a Healthy Cooking
When it comes to making healthy recipes in my kitchen, having the right kitchenware and utensils is a game-changer. It’s like my own little culinary workshop where I experiment with flavors and ingredients. With the right tools, here are some essentials I found that are helpful to have in your kitchen when creating healthy recipes.

Cooking Utensils Set | Baking Tray | Toaster | Bamboo Cutting Board | Dish Towels | Slow Cooker | Cookware Set | Pan Skillet Set | Salt & Pepper Grinder Set | Tea Kettle | Nutribullet Blender | Olive Oil Dispenser Bottle
Healthy High Fiber, High Protein Recipes
I’ve put together four different recipe books that all consist of healthy high-fiber, high-protein meals. These well-balanced recipes not only promote a sense of fullness but are also beneficial for weight loss. They offer delicious flavors along with an abundance of vitamins and minerals essential for your body. I hope you love them. You can purchase them a la carte or as a collection.
* Note: Most all recipes are gluten-free or can be made gluten-free.
Not all snack and dessert recipes are high-fiber and high-protein but they are healthier options and are for your enjoyment.




Essential Supplements & Vitamins to Include in Your Healthy Lifestyle
Supplements should not be a replacement for a healthy diet, however they can fill in the gaps and act like insurance. We should be getting most of our vitamins and minerals from a well-balanced diet high in nutrient-dense foods, as instructed above. If you’ve ever wondered what supplements are right for you or if you should take a probiotic, magnesium etc.. you may find my blog post on Essential Supplements for Women helpful.
My Nutrition & Lifestyle E-Book
If you’d like the full guide on how to live a healthy, happy, balanced lifestyle without all the rollercoaster diets and over exercising, check out my E-Book, Poised Health.
I hope this blog post has been informational for you. I’ve touched on how to eat a healthy diet, the benefits of a high fiber, high protein diet, how to make a healthy plate and featured my collection of healthy high fiber, high protein recipes. Remember you should always consult a doctor before starting any new diet or supplements. To learn more about living a healthy lifestyle and all my tips and tricks, my ebook is the way to go so be sure to check that out.



[…] Ultimate Guide to a High Fiber, High Protein Diet […]